Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a luxury in today’s competitive landscape but a must-have. AI in business applications automates monotonous jobs, uncovers hidden patterns, and more. Businesses that haven’t yet used the AI model are perplexed by model selection. However, AI’s efficiency dramatically depends on the appropriate model.
Selecting the best AI models for business is critical; using the wrong model, on the other hand, might result in inaccurate results, lost resources, and jeopardize your business goals. To help you make informed judgments on AI models, this post will provide you with the necessary knowledge and framework. Each model has unique characteristics, and understanding how to align them with your company goals is critical to success.
Generative AI And Its Benefits
An AI (Artificial Intelligence) model is a program that allows you to complete specified business tasks automatically without human participation. It can learn, solve problems, and make predictions like the human brain.
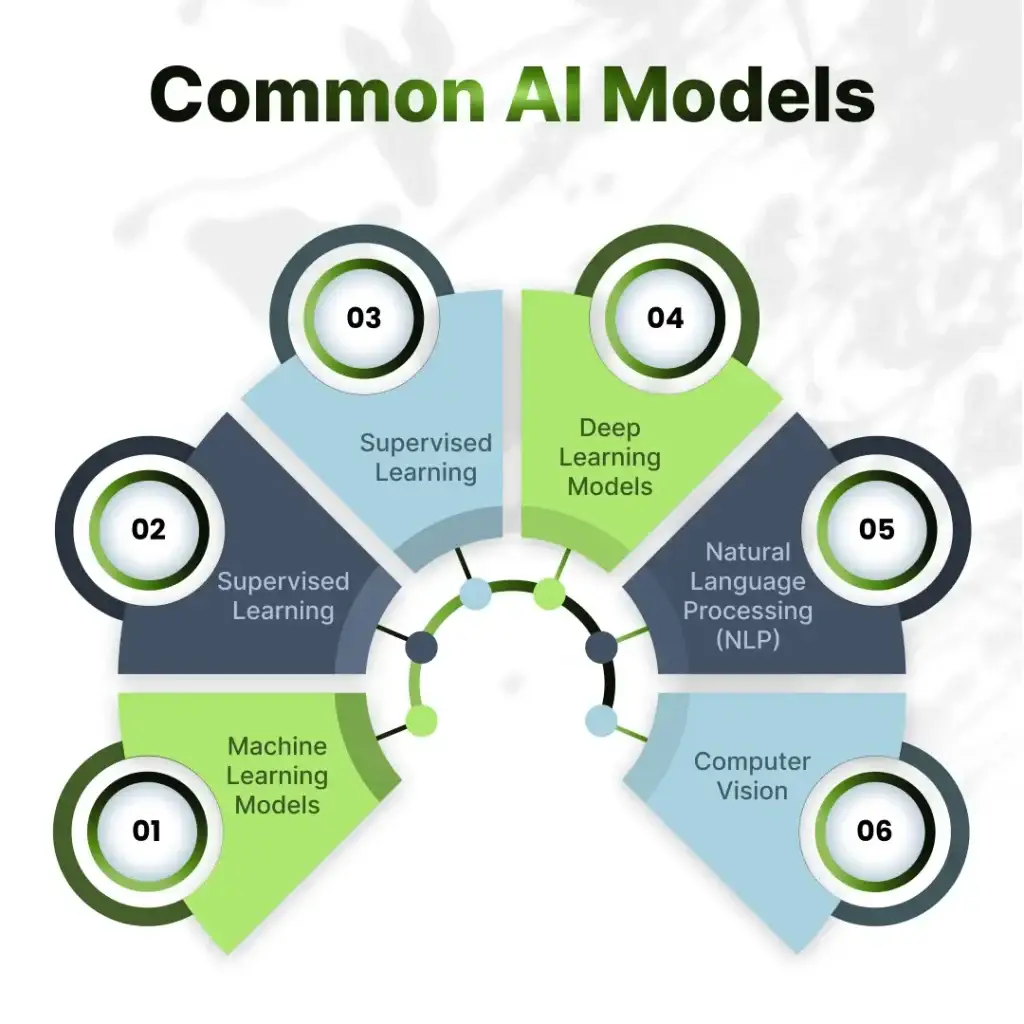
Unlike humans, AI models learn from massive datasets and utilize mathematical approaches and algorithms to derive insights. Let’s look at the six different AI models:
Machine Learning Models
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI technology that allows you to focus on creating a model capable of learning from massive amounts of data. ML models can recognize and find patterns in all data types. These models will eventually be able to anticipate results from test data.
Sometimes, machine learning exploits historical trends to improve efficiency; other times, it examines data, finds trends, and predicts what will happen. It can use its existing data to predict what will occur with additional data sets or draw conclusions about the future.
Supervised Learning
Supervised machine learning occurs when a neural network makes judgments or predictions using labeled data sets. To help guide the model, the programmers identified the data sets and entered important features and goal variables, teaching it to replicate human behavior. Humans, in a sense, provide the model with “training wheels” to aid decision-making.
This offers the model a structure to work with, making its predictions more accurate and lowering the possibility of errors. Companies can use supervised learning AI models to perform speech and text recognition, regression analysis, statistical testing, spam filters, fraud detection, KNN algorithms, K-means, and random forest algorithms.
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning involves removing the AI model’s “training wheels.” There is no human instruction, labeled data sets, or pre-existing relationships among data sets. The model must make judgments, whether with the assistance of another software program or entirely on its own.
As a result, the program is not limited to providing black-and-white, right-or-wrong answers; instead, it may perform more complex tasks such as data categorization. Unsupervised learning models are commonly used for trend analysis, grouping sentiments of social media posts, identifying traffic patterns, and detecting inefficiencies in industrial processes.
Deep Learning Models
Deep learning models are advanced machine learning techniques employing several layers of neural networks. It is helpful for activities that require vast amounts of data and complex interactions. These models are especially effective at handling enormous amounts of unstructured data. They are widely utilized in applications that require image recognition, natural language processing, and audio recognition.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is another machine-learning technology that analyzes, comprehends, and creates human language. As the volume of text data grows, NLP has become critical for extracting meaningful insights and automating various operations.
Transformers are a model that uses the self-attention mechanism to process and create text. They transformed NLP by enhancing its ability to manage long-term dependencies and content. Examples include BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformer) and GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer).
Token embeddings are a natural language processing technique for expressing words in a continuous vector space, with semantically comparable tokens clustered closer together. Examples include Word2Vec, GloVe, and FastText.
Computer Vision
A computer vision AI model is an intelligence software used to evaluate and comprehend visual information from photographs and videos. These models use machine learning algorithms, specifically deep learning approaches, to extract valuable insights from visual data.
They can perform various tasks, including object identification, picture classification, image segmentation, and facial recognition. A computer vision model, for example, can recognize objects in an image, classify images based on their content, and even track object movement in a video.
This technology has several applications, including driverless cars, medical imaging, surveillance systems, and robots.
Selecting the Right AI Model for your Business Objectives
Choosing the correct model is similar to selecting the perfect tool for a specific task—it can save time, improve results, and maximize resources. Incorrect choices, on the other hand, might lead to wasted investments and poor results. The AI model you select determines the performance of the Artificial intelligence application you intend to integrate with AI.
After conducting extensive study, we have compiled a list of essential characteristics to assist you in selecting the best AI model for your application. As a result, do not overlook any of the factors that may influence your decision.
Identify your Business Case
What are your organization’s special AI requirements or AI services for business? What challenges does your bespoke application want to solve? For example, you could automate customer care to reduce response time and increase customer satisfaction. Once specified, it will be easy to identify the extent and complexity of your AI requirements and connect them with your business objectives.
Challenges Your Company Faced
Once you’ve identified your company’s problem(s), choosing the right AI models for your business app will be easier. All that is required is solving issues based on input and output data.
Clearly describing your desired objectives, such as more revenue, lower expenses, or better operational performance, will help drive your model selection process. Consider your company limits, such as budget, available resources, data availability, and regulatory needs.
A solid grasp of your business requirements can help you select AI models aligned with your strategic aims and provide the most value.
Specifications for Performance
An AI model should balance speed, accuracy, and resource utilization to achieve business requirements. Legal document analysis and medical applications require high accuracy, meaning the model must emphasize precision over speed or computing economy.
Customer support models, on the other hand, must produce timely responses. It receives higher priority, and some loss of precision is acceptable.
Once you’ve decided what application to build next, follow the processes outlined to avoid problems and prepare to select the best AI model for your application.
Model Complexity
Complex models can handle intricate patterns but frequently require large amounts of data and computer capacity. Simpler models may be suitable for your purposes and provide shorter training times. We’ll help you find a model with the ideal blend of sophistication and efficiency.
Data type and size
The type and volume of your data (text, photos, statistics) will significantly impact your model selection. Some models flourish with large datasets, while others work better with smaller, more targeted sets. We’ll ensure your chosen model suits your specific data landscape.
Simple Integration
It is critical to interface easily with your current systems. We’ll choose an AI model with user-friendly APIs or deployment choices that work with your existing infrastructure, reducing disturbance and increasing productivity.
Data Access and Quality
AI models rely on data in the same way that an engine depends on fuel. You must ensure its quality, availability, and relevancy. Pay attention to data amount, variety, and cleanliness. If there are any gaps, inconsistencies, or quality issues, they must be addressed before AI implementation.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct AI model is a process that involves clarity, planning, and evaluation. Understanding your goals, data preparedness, and budget can help you select the ideal model for your organization. As with any growing technology, ongoing observation and adjustment are required.
By remaining current on the latest AI breakthroughs and collaborating with AI developers, you can ensure that your selected model continues to create value and move your organization forward.
Do you want to start a journey towards AI-powered app development? Our skilled team focuses on developing cutting-edge AI solutions. We use cutting-edge AI technologies to build creative and user-centric services, from intelligent chatbots to personalized suggestions.
Let us help you realize AI’s full potential and earn a competitive advantage. Contact us now for a free consultation!
FAQs: A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing Effective AI Models for Business Apps
1. Why is choosing the right AI model important for business apps?
Selecting the right AI model ensures that your business app efficiently solves specific problems, improves decision-making, and delivers a seamless user experience. The wrong model can lead to inefficiencies and poor outcomes.
What factors should I consider when choosing an AI model for my business app?
Key factors include the type of problem to solve, data availability and quality, scalability, integration capabilities, and cost-effectiveness of the model.
Which AI models are commonly used for business applications?
Popular AI models include machine learning algorithms (e.g., decision trees, random forests), natural language processing (NLP) models for chatbots and text analysis, and computer vision models for image recognition.