Best Offline Android Apps
Mobile business applications aren’t truly mobile if they can’t work offline on mobile devices, whether you’re using Android and iOS platforms. In today’s digital age, users expect their mobile apps, including offline apps, offline games, and tools like offline mapping, to function seamlessly even without internet access or a Wi-Fi connection. Until recently, organizations were faced with tripled time and cost when adding offline mode or offline access to a business app (Wired Magazine, June 2014).
Alpha Anywhere has transformed Android apps and iOS app development by enabling businesses to build offline-first architecture with ease. Developers can now enjoy building hybrid mobile apps and cross-platform development projects without incurring extra cost or effort. Whether it’s Progressive Web Apps (PWA), local data storage, or advanced data synchronization with conflict resolution, Alpha Anywhere offers all the essential tools to ensure apps work even without an internet connection.
Its platform supports NoSQL mobile databases, uses service workers for smooth offline functionality, and helps optimize mobile app performance for better user experience. This ensures users can enjoy their favorite features, pass the time, or access essential tools regardless of network conditions—without sacrificing space on your device or relying heavily on streaming services like Google Maps.
Watch the 90-second demo video to learn how Alpha Anywhere enables offline mobile application development that truly works—anytime, anywhere.
No matter how good a developer you are, you would require something to support your app offline. On this page, you will get to know about the offline mobile application architectures for iOS and Android Apps with which you can develop robust apps that can tackle offline capabilities in the best way.
Have you ever thought about why you have to design an app for the offline experience? Offline mobile app architecture is the most important thing that every developer should consider. Sometimes networks die and the networks are low and there are even more factors that will often need offline support. If your apps have users operating from different parts of the world then you need to account for the offline support or experience even more. Even if you are a good developer, in most cases you will require something to support your app offline. Everything depends upon what your app does; it might be simple or complicated sometimes.
You probably already have Google Maps on your phone, one of the best offline Android apps available. What you might have missed out on, however, is its ability to guide you even without an internet connection. As an offline mobile app, Google Maps lets you download maps for a particular region locally on your phone.
So next time you’re stranded in an unfamiliar area, you won’t have to worry about your cellular bars. In addition to navigation, these offline maps allow you to look up hotels and landmarks, making it an essential offline mobile app.
To download a location’s offline maps, launch the Google Maps app on your phone and search for the place you’re headed to. In its information card, you’ll find an option labeled Download. Hit that, select the area to download, and tap Download again to save it.
What Is Offline Mobile App Architecture?
Build Android and iOS offline apps with Alpha Anywhere that includes powerful features for modern mobile apps. Enjoy building robust android apps that work on any mobile device, even without internet access or a stable internet connection or Wi-Fi. These apps allow users to enjoy your favorite tools and features—like Google Maps, offline games, or offline mapping—to pass the time efficiently, all while saving space on your device and reducing reliance on streaming services.
Alpha Anywhere supports Offline-First Architecture, enabling developers to build resilient applications using Progressive Web Apps (PWA) technology. It offers fine-grained conflict resolution in offline mode, going beyond basic “last-write wins” logic. It also features local data storage, allowing apps to store and access databases, documents, drawings, and videos directly on the device when there’s no signal.
Your app maintains data persistence even if it is closed or the battery dies—ensuring unsaved data is never lost. Built-in support helps convert SQL data into hierarchical JSON datasets (e.g., customers, their orders, and order details). It can store data, display transactions (including changes, errors, and updates), and synchronize offline transactions back to the server with efficient data synchronization capabilities.
Alpha Anywhere allows incremental data downloads, granular multi-transaction synchronization, and supports mobile app performance optimization through features like Service Workers, NoSQL Mobile Databases, Hybrid Mobile Apps, and Cross-Platform Development. It also caches offline data by automatically generating a manifest file, leveraging the browser’s App Cache to persist HTML, CSS, and other web app assets.
If you have to know about offline architectures for iOS and Android apps, it really takes more than 20 programming books to get you there. No matter whether you are a developer or a CEO or even a product manager, trying to understand how your app could behave offline is very important and will serve you more things in the future. First of all, it is important to understand the three broad categories of offline apps.
- Data is stored offline where there is no editing functionality. For this, you can consider the example of GPS data where the data is being stored offline temporarily
- The users can edit their data offline and once they are back online they can sync their details. For this, a note-taking app will be a great example
- The users can edit other data offline. For this, you can imagine edits to an offline Google doc type application
In this, you could see some offline mobile architectures to develop robust apps, and with these how you can build an application that can tackle the offline capabilities.
Trello’s offline architecture story

Trello did not support offline apps in 2016, and its users were complaining heavily about this issue. Many relied on mobile apps like Trello while commuting, often in subways where internet access or Wi-Fi was unavailable. Users wanted to enjoy your favorite productivity tools even without an internet connection, especially on their mobile device. The initial app architecture for Android and iOS assumed constant connectivity, leaving users helpless during network disruptions.
The lack of offline mode meant users couldn’t organize tasks or use key features unless online. Frustrated by this limitation, Trello made a critical shift to an Offline-First Architecture, ensuring the app would function reliably in all conditions. In the upgraded version for Android apps and iOS, local data storage through a local database became central. This allowed data to be stored on the device, enabling access to information and tasks during offline periods.
The transition included implementing service workers, NoSQL mobile databases, and advanced data synchronization strategies. This change not only enabled Trello to sync data effectively when back online but also offered conflict resolution features to manage edits made during offline sessions. With the adoption of Progressive Web Apps (PWA) principles, hybrid mobile apps, and cross-platform development, Trello ensured better mobile app performance optimization.
Application architecture without offline considerations
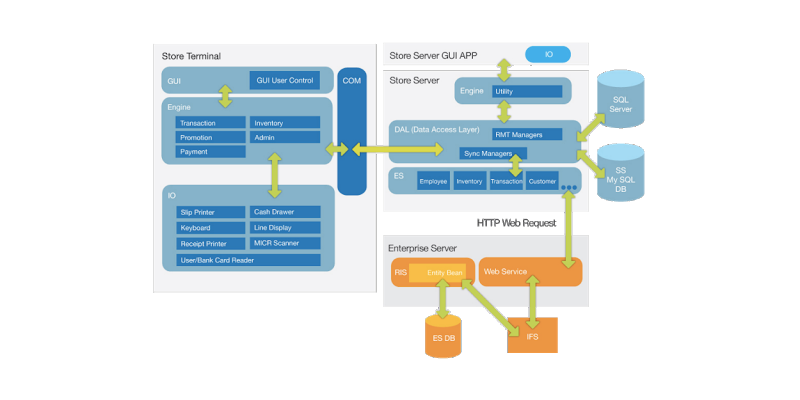
In this, you can see about the retrofit because a lot of developers use it as their data model. In architecture for iOS and Android apps, the view model relies on the network or the server to work. If there is no network then nothing can happen on the mobile and for the end-user, it might seem like the app is stuck in between.
If there is no network in the place then the application’s user interface would suffer from the pending request and would behave in absence of internet connectivity.
To improve this condition it is highly advisable to place a model within the app. Most of the clients will come with apps that have no model in place. But it should not be the case when you create an app.
Improving the architecture a bit
Here is a minimal improvement that can be done to improve the quality of the app. First, it is important to introduce a model. For example, you can consider the newsfeed app in which your user reads something interesting and wants to add a comment. You have to place a model with your app and see how you feel. Till the comment gets synchronized it will appear in a light color and when it gets fully synchronized it will turn into a dark color.
Evolution 2 and 3 Offline mobile app architecture
At some point in time, the developers noticed the shortcomings and started to introduce the local cache to their app. This was actually to work in the offline scenarios.
Here you can consider the same news feed app but also with a context to android. Usually, the developers handle the cache and this is done via the shared preferences or the SQLite database.
Dedicated cache service
In this, the cache is applied to the architecture with the dedicated cache service. By doing this the developers can include the HTTP requests locally.
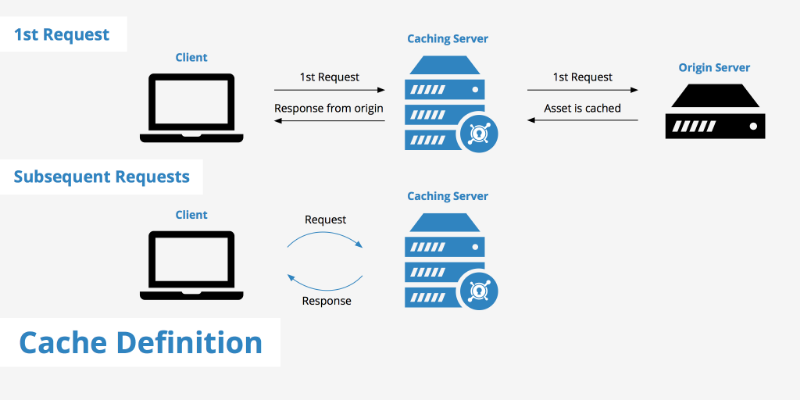
Cache applied to the presenter
In the modification, the cache is applied to the presenter.
With both of these, it seemed to work for the low complexity cases. If you are building an app that has a substantial user base then it may not be able to work properly. Also, you can frequently see some implementation errors.
Evolution 4 and 5 Offline mobile app architecture
A Progressive Web App (PWA) is a web app that tries to replicate the behavior of a native app. They’re designed for quick loads, push alerts, and use while offline or with poor network access. PWAs are similar to native applications in that they may be installed on a user’s device. However, they are developed using standard web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
As a result, consumers no longer need to download an app from an app store. Also, PWAs are more accessible and more straightforward to produce than native applications. PWAs provide the conveniences of a native app while still being accessible through a web browser. To close the gap between native applications and the web, PWA strives to provide a unified and consistent user experience. With PWAs, business owners can avoid the battle of choosing between a native app vs hybrid app.
Built-in, Automatic Use of Local Storage to Persist Data and State
When building mobile apps for Android and iOS, especially those that support offline mode, it’s crucial to ensure that any changes made by the user while offline are preserved. This is essential when using offline apps, offline games, or offline mapping tools on a mobile device, particularly in areas with no Wi-Fi or internet access. Users expect to enjoy your favorite apps and pass the time without disruption—even when power is lost or connectivity drops.
Alpha Anywhere makes it incredibly easy to use local data storage to persist user data and app state. This ensures that all changes made in offline mode are retained and safely synchronized back to the server once an internet connection is available. Whether you’re working on android apps, planning trips on Google Maps, or accessing content typically reliant on streaming services, Alpha Anywhere provides seamless offline functionality.
This approach supports a true Offline-First Architecture, using service workers, NoSQL mobile databases, and data synchronization mechanisms to protect data. It’s ideal for developers working on hybrid mobile apps or cross-platform development, ensuring smooth user experiences across devices. With features tailored for mobile app performance optimization, Alpha Anywhere helps save space on your device while delivering reliable, responsive apps—even in disconnected environments.
In the modification, the cache is applied to the presenter.
With both of these, it seemed to work for the low complexity cases. If you are building an app that has a substantial user base then it may not be able to work properly. Also, you can frequently see some implementation errors.
The persistent offline architecture
While caching HTTP requests it might seem like a good solution. The issue with most of the HTTP requests is that you basically start with an empty model when you leave an app and come back. If your model is empty it can’t fetch anything that you have in your cache memory.
How do you fix this?
You have to change it to a persistent model. First start by persisting data on disk, by doing this the application can have the data if the user leaves the application. Also, use something called application logic with this you can make the network calls and keep the persistent model up to date.
Whenever the application logic does that it notifies and can be built on top of RX or on whatever you prefer. As soon as it fetches the information it shares it with the persistent model. This information can be then used by the entire application. Whatever component needs the information, the component can directly request the information from the persistent model.
Space for further optimizations
Now you have allowed a user to post the comment in the zero network conditions. But what you can do when your user wants to post three consecutive comments. With the architecture, the comments could appear at once and this is a sort of poor user experience. For all this, you have to look at the process flow and see how things are happening. You can implement these with the queues and separate them by the network and local queues. Now when the user adds comments in the comment section the app that you have created will not behave as it did with the previous cases.
What offline mobile app architecture to use?
The offline architectures are better suited for e-commerce apps, Real-time apps. News apps and map apps. The reasons are, it can bring faster data retrieval after sending the first request and can handle the connectivity better. Ahead of time, the offline architectures are used for note-taking apps, email apps, weather apps, finance-type apps, and messaging apps.
Offline – online sync: architectural considerations
If you are not sure about what offline considerations you have to keep in the mobile app, here are a few things that your offline architecture should support,
- How and where you are going to cache your data?
- To what extent is caching reliable?
- How is the architecture going to handle concurrency?
- Is there any safeguard in your architecture to handle the data conflicts?
- How can this architecture handle the connectivity changes?
This blog can help you in many ways to know about offline architectures for for iOS and Android apps. But this is not sufficient if you are a developer. Make sure you get to about these before you develop an app.
FAQs
What is an offline mobile app?
An offline mobile app allows users to access key features and data without an active internet connection.
Why build an offline-capable app?
Offline support improves user experience in areas with poor connectivity and ensures uninterrupted app usage.
How do offline apps store data?
They use local storage methods like SQLite, Core Data, Realm, or file systems depending on the platform and complexity.